
What could explain these crazy results? After all, whole milk doesn't just have more fat it also has almost twice as many calories. Central obesity is actually a really important measure, too, because it's strongly associated with cardiovascular disease and diabetes. They looked at the kind of dairy that 1,500 men had in their diets and were amazed to see that the dudes who didn't eat any butter and chose low fat were 50% more likely to develop a central obesity (essentially, a beer belly), while those who ate butter and drank whole milk were 50% less likely to get a gut, compared to men whose diets were in the middle. Some scientists in Sweden decided to get to the bottom of the milk misconceptions. Milk wasn't the only victim of the low-fat craze, which in general didn't do waistlines any favors. Whole milk might actually be linked to less obesity Strangely, the whole milk that had been around for centuries had never caused heart disease before, but it sounded like a good hypothesis anyway. It's a misguided, vestigial notion that dates back to those days when fat-especially the saturated fat in animal products like milk- was to blame for all the chronic diseases people seemed to be acquiring, like obesity, heart disease, and diabetes. The only problem with this logic is that drinking full-fat milk doesn't actually give you heart disease. So, Eisenhower-era Americans and beyond were given a few choices: drink white-colored water and be really healthy, drink creamy goodness the way our forefathers did and get heart disease, or take a middle-of-the-road approach by drinking milk that tastes OK and might be a little bit bad for your health. Like any good war-fueled industry with loads of extra product on its hands after the conflict ends, the dairy producers found ways to sell their goods: they convinced doctors to recommend reduced-fat milk, and who doesn't enjoy a good doctor recommendation?
Rather than making its way into the homes of average Americans, though, it was more commonly used as a feed to fatten pigs for market, which is kind of gross.Īs Kendra Smith-Howard explains in Pure and Modern Milk, World War II came along and increased the demand for powdered skim milk. Skim milk's journey from pig fattener to health foodĭespite the obvious post-World War II connection to fat- and health-conscious consumers, skim milk was actually around much earlier as a byproduct of butter production.
Skim milk meaning full#
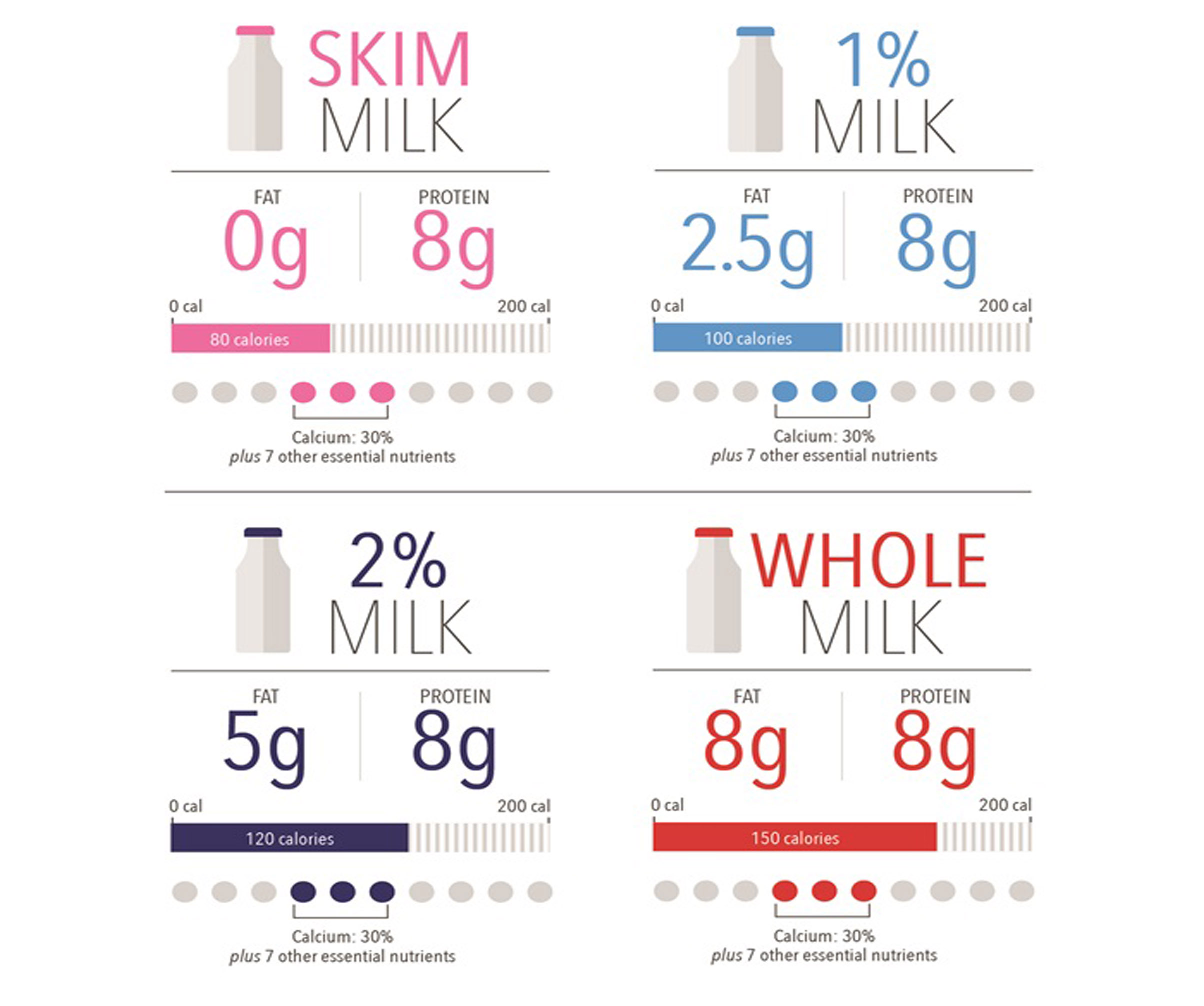
"Whole" milk sounds like it's full of cream, but it's actually just over 3% fat-dairy producers probably just leave that off the bottle for fear that grocery shoppers will get confused with so many numbers. Yep, there's probably an ACT math problem for this.

For skim milk, your dairy producer literally skims the cream off the top and leaves it out, whereas with 1% or 2% milk they're taking it out and adding some back in until it's 1% or 2% of the total volume.

Milk producers take the cream out of the milk, then put some of it back in, depending on what label you want to stick on the carton. Separation is a little different, though. Some people argue that we should skip all of these and campaign for hippie-friendly " raw milk." You can think of it as trendy, or you can acknowledge that when you skip the pasteurization and homogenization, you're really getting something that's potentially disease-causing and lumpy-whatever floats your boat. But there are a few steps with long names between the cow and the consumer: pasteurization, homogenization, and separation. It's still coming from cows, don't worry.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
